Table of Contents
ToggleCan Vitamin B12 Deficiency Be a Sign of Cancer an Early Warning?
Image Credit: Care Hospitals
Introduction:
Vitamin B12 plays a critical role in maintaining the health of your nerves, blood cells, and DNA synthesis. It’s one of the essential nutrients that the body can’t produce on its own, relying solely on dietary intake or supplements. A deficiency in Vitamin B12 may cause a range of symptoms, from fatigue and weakness to serious neurological issues. But could it also be an early warning sign of something as serious as cancer? This article explores the potential link between Vitamin B12 deficiency and cancer, offering insights into why monitoring your B12 levels is crucial for overall health.
Read Also: cancer diagnosis for 80s rocker : A Look at Their Journey
Understanding Vitamin B12:
What is Vitamin B12?
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin crucial for various physiological functions. It is particularly vital for the formation of red blood cells, proper brain function, and DNA synthesis.
Sources of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is primarily found in animal-based foods, such as:
- Meat and poultry.
- Fish and shellfish.
- Eggs and dairy products.
For those on plant-based diets, fortified cereals or B12 supplements are often necessary to meet daily requirements.
Role of B12 in the Body
Vitamin B12 supports the development of red blood cells, ensuring oxygen is efficiently transported throughout the body. It also helps maintain nerve health and cognitive functions, making it indispensable for overall well-being.
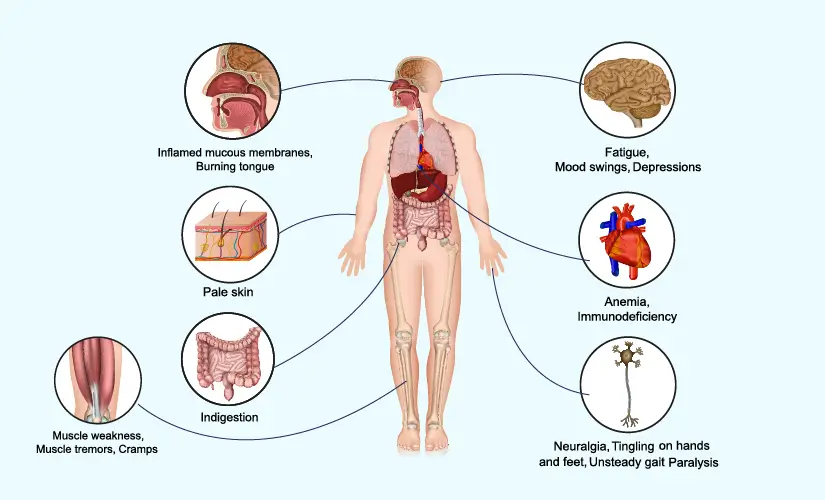
Common Symptoms of Vitamin B12 Deficiency:
Physical Symptoms
A lack of B12 can manifest in noticeable physical signs such as:
- Fatigue and weakness.
- Pale or jaundiced skin.
- Shortness of breath or dizziness.
Neurological Symptoms
When left untreated, B12 deficiency can affect the nervous system, causing:
- Tingling or numbness in hands and feet.
- Memory issues and difficulty concentrating.
- Depression or mood changes.
Chronic Issues Linked to Deficiency
Persistent B12 deficiency has been linked to anemia, cardiovascular problems, and increased susceptibility to infections.
Link Between Vitamin B12 Deficiency and Cancer:
How Deficiencies Are Connected to Underlying Health Problems
Vitamin B12 deficiency isn’t a standalone condition—it often points to deeper health concerns. For instance, poor absorption due to gastrointestinal disorders may highlight the presence of certain cancers.
Types of Cancer Potentially Associated with B12 Deficiency
Studies suggest that certain cancers, such as stomach and colorectal cancers, may impair the body’s ability to absorb B12, leading to noticeable deficiencies.
Early Warning Signs of Cancer:
Recognizing Subtle Changes in the Body
Cancer often starts with subtle, easy-to-miss symptoms. In the context of Vitamin B12 deficiency, unexplained fatigue or persistent digestive issues may warrant closer examination.
Why B12 Levels Might Decrease During Cancer Onset
Cancer can interfere with how the stomach absorbs nutrients, leading to deficiencies. Additionally, some cancers metabolize B12 at a higher rate, depleting its reserves in the body.
Read Also: cancer diagnosis for 80s rocker : A Look at Their Journey
The Role of Pernicious Anemia:
What is Pernicious Anemia?
Pernicious anemia is a condition that occurs when the body cannot properly absorb Vitamin B12 due to a lack of intrinsic factor—a protein produced in the stomach. This condition can cause severe B12 deficiency over time. Since pernicious anemia is often linked to autoimmune disorders, it may also raise concerns about underlying health problems, including an increased risk of cancer.
Its Association with Cancer Risks
Pernicious anemia has been correlated with a higher risk of stomach and gastric cancers. The autoimmune nature of this condition may cause chronic inflammation in the stomach lining, which could potentially lead to cellular changes and, in rare cases, malignant transformations.
Diagnosing Vitamin B12 Deficiency:
Blood Tests and Biomarkers
To determine if you are deficient in Vitamin B12, doctors typically order blood tests that measure:
- Serum Vitamin B12 levels.
- Homocysteine levels.
- Methylmalonic acid (MMA) levels, which often rise when B12 is deficient.
Identifying Causes Beyond Dietary Habits
B12 deficiency isn’t always caused by a lack of dietary intake. It can result from:
- Gastrointestinal conditions like Crohn’s disease or celiac disease.
- Surgical procedures that affect the stomach or intestines, such as gastric bypass.
- The presence of tumors in the stomach or intestines, which may interfere with nutrient absorption.
Is Vitamin B12 Deficiency a Definitive Sign of Cancer?
Exploring the Correlation and Causation Debate
While Vitamin B12 deficiency may signal an underlying issue, it’s not always directly linked to cancer. The relationship is more about correlation rather than causation. Low B12 levels can occur due to other non-cancerous conditions, such as chronic digestive issues, making it essential to explore all possible causes.
Other Health Conditions Mimicking Similar Signs
Several conditions can present symptoms similar to B12 deficiency, such as hypothyroidism or multiple sclerosis. This is why comprehensive testing is crucial for a proper diagnosis.
Cancer Types and Their Association with B12 Levels:
Stomach and Gastrointestinal Cancers
Cancer of the stomach or intestines can directly impact the body’s ability to absorb nutrients, including Vitamin B12. Tumors may block absorption or disrupt the production of intrinsic factor, leading to deficiency.
Leukemia and Lymphoma
Hematologic cancers like leukemia and lymphoma can cause elevated demands for B12 due to rapid cell turnover. In these cases, B12 deficiency may exacerbate anemia, which is already a common symptom in these cancers.
How Cancer Affects Vitamin Absorption:
Tumors Disrupting Nutrient Absorption
Cancers in the digestive tract, such as colorectal cancer, can interfere with normal absorption processes. This is particularly true if the tumor grows in areas responsible for nutrient uptake.
Chemotherapy and Its Impact on Vitamin Levels
Cancer treatments like chemotherapy can further deplete Vitamin B12 levels. These treatments often target rapidly dividing cells, including those in the gut lining, impairing the body’s ability to absorb nutrients effectively.
Prevention and Monitoring of B12 Levels:
Regular Health Check-Ups
Routine blood tests can help monitor your B12 levels, especially if you’re at risk for deficiency due to dietary restrictions or medical conditions. Early detection can prevent complications.
Diet Tips for Maintaining Adequate Levels
To prevent deficiency, incorporate Vitamin B12-rich foods into your diet, such as:
- Lean meats and fish.
- Eggs and dairy products.
- Fortified cereals or plant-based milk alternatives for vegans.
When to Seek Medical Advice:
Recognizing Persistent Symptoms
If you experience persistent fatigue, numbness, or cognitive difficulties, it’s time to consult a healthcare professional. These could be signs of a serious underlying issue.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early detection of Vitamin B12 deficiency and its root cause can make a significant difference in outcomes, particularly if cancer is involved. Timely intervention can lead to better treatment options and a more positive prognosis.
Treatment Options for Vitamin B12 Deficiency:
Dietary Changes
Increasing your intake of B12-rich foods can often resolve mild deficiencies. For vegetarians and vegans, fortified products or supplements are essential.
Supplements and Injections
In cases where absorption is impaired, doctors may recommend B12 injections or high-dose oral supplements to bypass the digestive system.
Living with Vitamin B12 Deficiency:
Managing Long-Term Health
If your deficiency is caused by a chronic condition, such as pernicious anemia or cancer, ongoing management will likely involve regular monitoring and supplementation.
Addressing Recurring Symptoms
It’s essential to address recurring symptoms promptly. Ignoring them can lead to irreversible nerve damage or other long-term complications.
Read Also: dwp benefit claimants bonus payments: A Comprehensive Guide
Conclusion:
Vitamin B12 deficiency can be an early warning sign of underlying health problems, including cancer, but it is not a definitive indicator. The connection lies in how certain cancers, particularly those affecting the stomach and intestines, interfere with nutrient absorption. Understanding your symptoms, seeking timely medical advice, and maintaining a balanced diet are key to addressing B12 deficiency effectively. Early detection and intervention are crucial to prevent complications and ensure overall well-being.
FAQs:
1. Can a B12 deficiency always indicate cancer?
No, Vitamin B12 deficiency has various causes, including dietary habits, pernicious anemia, and gastrointestinal disorders. Cancer is just one possible cause.
2. What cancers are most commonly linked to B12 deficiency?
Cancers of the stomach, intestines, and blood (such as leukemia and lymphoma) are most commonly associated with B12 deficiency due to absorption issues or increased demand for the vitamin.
3. How is Vitamin B12 deficiency diagnosed?
Doctors use blood tests to measure B12 levels, homocysteine, and methylmalonic acid (MMA) levels. A physical exam and medical history also aid in diagnosis.
4. Can I prevent Vitamin B12 deficiency with supplements?
Yes, supplements or fortified foods can prevent deficiency, especially for people at risk, such as vegans or those with gastrointestinal disorders.
5. Is Vitamin B12 deficiency reversible?
In most cases, yes. Early intervention with dietary changes or supplements can effectively restore Vitamin B12 levels. However, prolonged deficiency may cause irreversible nerve damage.